Jeep XJ Engine For Sale: Your Ultimate Guide to Buying, Replacing, and Maintaining
Jeep XJ Engine For Sale: Your Ultimate Guide to Buying, Replacing, and Maintaining /jeeps.truckstrend.com
The Jeep Cherokee XJ, produced from 1984 to 2001, stands as an enduring icon in the automotive world. Renowned for its rugged simplicity, impressive off-road capability, and surprising on-road manners, the XJ has cultivated a fiercely loyal following. At the heart of its legendary status, particularly for the later models, lies the venerable 4.0-liter inline-six (I6) engine. This powerplant, celebrated for its durability, torque, and relative ease of maintenance, is often the reason XJ owners cling to their vehicles for decades.
However, even the most robust engines eventually show their age. Whether due to high mileage, catastrophic failure, or the pursuit of a new project, the need to find a "Jeep XJ engine for sale" is a common quest for many enthusiasts. This comprehensive guide will navigate you through everything you need to know about purchasing, evaluating, and understanding the nuances of acquiring a replacement engine for your beloved Jeep XJ, ensuring your adventure continues for miles to come.
Jeep XJ Engine For Sale: Your Ultimate Guide to Buying, Replacing, and Maintaining
Why Buy a Jeep XJ Engine? Common Scenarios
Before diving into the "how," it’s important to understand the "why." Owners typically seek a replacement XJ engine under several circumstances:
- Engine Failure: The most common reason. This could stem from a thrown rod, cracked block, severe overheating leading to head damage, or complete loss of compression across cylinders. While the 4.0L is tough, neglect, poor maintenance, or extreme conditions can take their toll.
- High Mileage Exhaustion: Even if not catastrophically failed, an engine with 200,000+ miles might be tired. Symptoms like excessive oil consumption, persistent knocking noises, low oil pressure, or a significant drop in power can signal it’s time for a refresh or replacement.
- Project Vehicle or Restoration: For those building a custom off-roader, restoring a classic XJ, or swapping the engine into another Jeep model (like a Wrangler YJ), a good donor engine is essential.
- Performance Upgrade (Less Common for XJ): While less typical for a direct XJ engine replacement (as most upgrades involve modifying the existing 4.0L), some might seek a newer, lower-mileage 4.0L as a fresh foundation for performance modifications.

Understanding the Jeep XJ Engine – The Legendary 4.0L I6
The star of the show is undoubtedly the 4.0-liter AMC Straight-6 engine. Introduced in 1987, it quickly became the definitive engine for the Cherokee. Known for its under-stressed design, ample low-end torque, and an almost bulletproof reputation, it’s a major reason for the XJ’s longevity.
Key Variations to Note:
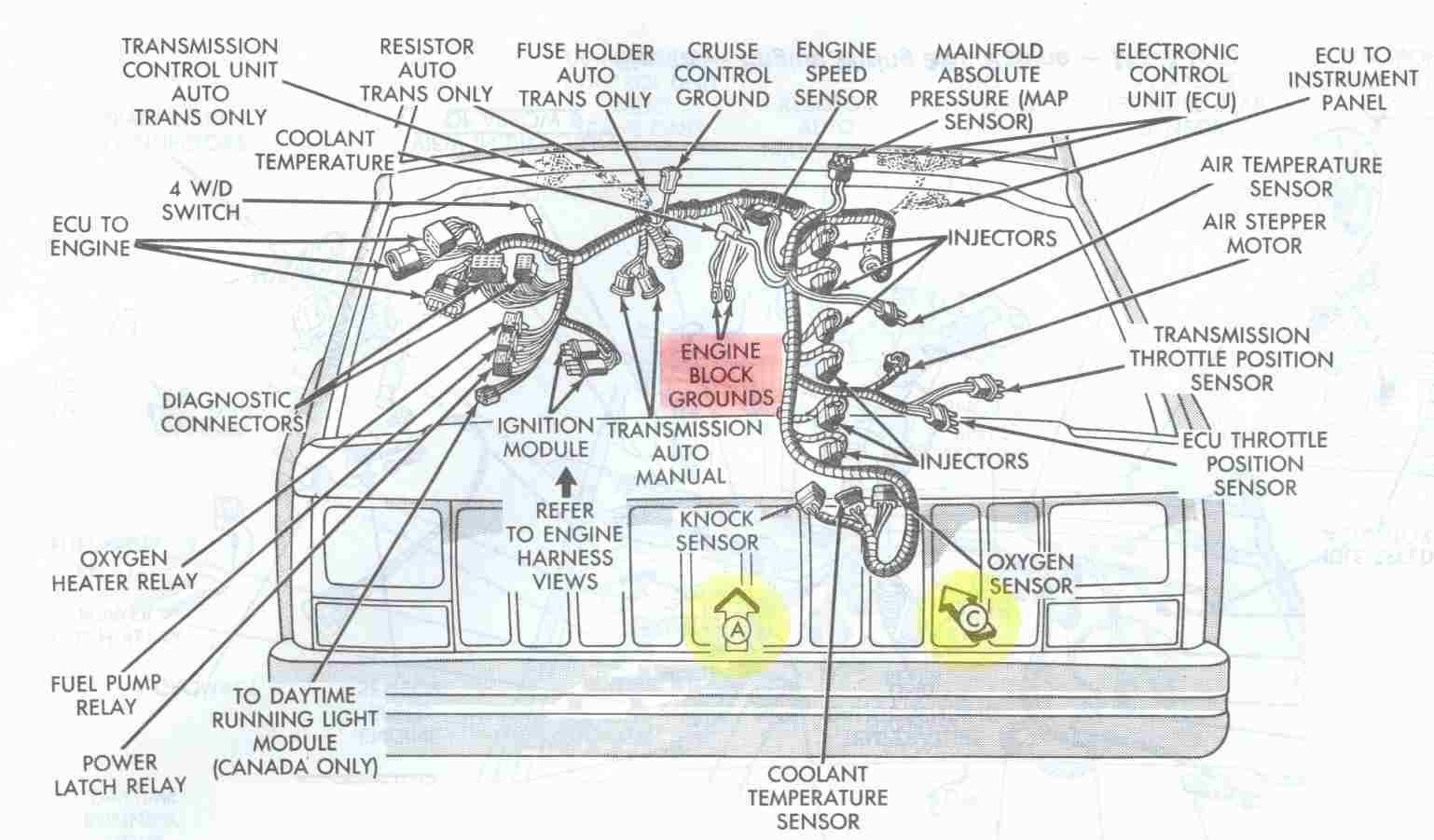
- Renix Era (1987-1990): These early 4.0L engines used a Renault-Bendix (Renix) engine management system. They are known for being slightly less powerful (177 hp) and having a different sensor array and wiring harness compared to later models. Swapping a Renix engine with an HO or vice-versa requires significant electrical and sensor modifications.
- High Output (HO) Era (1991-2001): The HO version, introduced in 1991, featured a revised cylinder head, intake manifold, and a Chrysler-designed engine management system (OBD-I, then OBD-II). This bumped horsepower to 190 hp. The HO engines are generally more desirable due to their power and more common parts availability.
- Distributor vs. Coil-on-Plug: Earlier HO models (up to 1999) used a traditional distributor. From 2000-2001, the engine moved to a coil-on-plug ignition system with a revised cylinder head, making these later engines slightly more complex to swap into older vehicles without significant modifications.

While the 2.5L inline-four and various V6 engines (like the GM 2.8L and Renault 2.1L diesel) were offered in early XJs, the 4.0L I6 remains the most sought-after and supported engine for replacement.
Where to Find a Jeep XJ Engine For Sale
The hunt for a suitable XJ engine can take you to several places, each with its own pros and cons:
-
Online Marketplaces:
- eBay: A vast selection, from individual sellers to commercial dismantlers. Offers buyer protection but shipping can be complex and expensive.
- Facebook Marketplace & Groups: Excellent for local finds, often from private sellers or smaller shops. Look for dedicated Jeep XJ groups where enthusiasts frequently buy/sell parts.
- Craigslist: Similar to Facebook Marketplace for local deals, but exercise caution and meet in safe, public places.
-
Specialized Salvage Yards/Junkyards:
- LKQ Pick Your Part & Other Large Chains: These yards often have sophisticated inventory systems and can locate engines across their network. They might offer limited warranties.
- Local Auto Recyclers/Dismantlers: Good for finding a complete donor vehicle or just the engine. Building a relationship with a local yard can yield good results.
-
Dedicated Jeep Forums & Communities:
- NAXJA (North American XJ Association), Cherokee Forum: These online communities have "For Sale" sections where members often sell engines they’ve pulled from parts Jeeps or upgrades. You’re dealing with fellow enthusiasts, which can be a plus.
- Local Off-Road Clubs: Networking within local Jeep communities can lead to leads on engines from project vehicles or parts Jeeps.
-
Remanufactured Engine Suppliers:
- Jasper Engines & Transmissions, ATK, S&J Engines, etc.: These companies specialize in professionally rebuilt engines. They come with warranties, are typically tested, and offer a much higher degree of reliability than a used engine. They are, however, significantly more expensive.
- Local Engine Rebuilders: A good option if you want to support local businesses and can often get a custom build or rebuild your existing core.
Types of Jeep XJ Engines Available (Condition-wise)
Understanding the different types of engines available will help set your expectations and budget:
-
Used/Salvage Engines:
- Pros: Most affordable option. Can sometimes find low-mileage gems from wrecked vehicles.
- Cons: Unknown history. No warranty (or very limited). Risk of hidden issues. Requires thorough inspection.
- What to Ask For: Mileage, year of donor vehicle, VIN (if possible), compression test results (if available), video of it running (if still in the vehicle).
- Pricing: Typically ranges from $300 (high mileage, unknown condition) to $1,500 (lower mileage, verifiable condition).
-
Rebuilt/Remanufactured Engines:
- Pros: Comes with a warranty (often 3 years/100,000 miles). All wear components replaced (bearings, rings, gaskets, seals). Machined to factory specs.
- Cons: Significantly higher cost than used. Requires core exchange (your old engine) or a core charge.
- What to Look For: Reputable rebuilder, detailed warranty terms, what components are included (long block, short block, accessories).
- Pricing: Ranges from $2,000 to $4,000+, depending on the supplier and specifics.
-
New Crate Engines (Very Rare for XJ 4.0L):
- Pros: Zero miles, brand new components, often performance-oriented.
- Cons: Extremely expensive, often custom-built. Not a common "off-the-shelf" item for a stock XJ.
- Pricing: Typically $5,000 and up, often much higher for performance builds.
Important Considerations Before Buying
A successful engine swap starts with a smart purchase. Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Budget: Don’t just factor in the engine cost. Add shipping, a core charge (if applicable), fluids, new gaskets, hoses, sensors, spark plugs, and potentially a new water pump, thermostat, and motor mounts. If you’re paying for labor, that’s a significant expense.
- Compatibility (Renix vs. HO, Year Matters!): This is paramount.
- 1987-1990 (Renix): Unique sensors (MAP, TPS, CPS), wiring harness, and ECU. Swapping a Renix into an HO XJ or vice-versa is a major undertaking involving electrical conversion.
- 1991-1999 (HO, Distributor): Most common and interchangeable. Sensor locations are generally consistent.
- 2000-2001 (HO, Coil-on-Plug): Features a different cylinder head, exhaust manifold, and coil-on-plug ignition. Swapping these into older XJs requires significant modification to the wiring and potentially the ECU.
- Always verify the exact year of the donor engine and ensure it matches your XJ’s requirements or that you’re prepared for modifications.
- Shipping & Logistics: Engines are heavy. Freight shipping is expensive and requires special handling (e.g., liftgate service for residential delivery). Factor this into your budget and plan for how you’ll unload it.
- Warranty: For used engines, expect "as-is" or a very limited 30-90 day warranty (often parts only, not labor). Remanufactured engines typically come with a substantial warranty. Understand its terms and conditions thoroughly.
- Inspection (for Used Engines):
- Visual Check: Look for signs of severe impact damage, cracks, or excessive corrosion.
- Oil Condition: Check the dipstick. Brown oil is fine; milky oil indicates coolant in the oil (bad head gasket or cracked block/head); extremely thick, sludgy oil indicates neglect.
- Spark Plug Holes: Look into them with a flashlight. Are the cylinder walls rusty?
- Mounting Points: Check for stripped threads or damage.
- Crankshaft Rotation: Try to manually turn the crankshaft (if accessible) to ensure it’s not seized.
The Installation Process (Overview)
While a full step-by-step guide is beyond this article’s scope, here’s an overview of what an engine swap entails:
- Preparation: Gather tools (engine hoist, stand, socket sets, wrenches, torque wrench), drain fluids, disconnect battery.
- Disassembly: Disconnect all hoses, wires, exhaust, accessories (alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor), transmission, and motor mounts.
- Removal: Carefully lift the old engine out of the engine bay using an engine hoist.
- Transfer Components: Many engines are sold as "long block" (block, head, oil pan, valve cover). You’ll need to transfer your existing intake manifold, exhaust manifold, accessory brackets, sensors, and sometimes the flywheel/flexplate to the new engine.
- Installation: Lower the new engine into place, connect to the transmission, bolt down motor mounts, and reattach all accessories, hoses, and wiring.
- Initial Startup: Fill with fresh oil and coolant. Prime the oil pump (if possible). Start the engine, listen for unusual noises, check for leaks, and monitor gauges. Perform a proper break-in procedure if it’s a rebuilt engine.
Tips for a Successful Engine Purchase & Swap
- Do Your Homework: Research the seller, read reviews, and verify their legitimacy.
- Ask Detailed Questions: Don’t be afraid to ask about mileage, maintenance history, reason for removal, and what exactly is included with the engine.
- Get it in Writing: Ensure all terms, including warranty, core charge, and included components, are clearly stated on an invoice or agreement.
- Factor in Ancillary Costs: Budget for new gaskets, seals, spark plugs, fluids, a new thermostat, and potentially a new water pump and motor mounts. It’s much easier to replace these while the engine is out.
- Consider Upgrades: While the engine is out, it’s a perfect time to upgrade the radiator, hoses, or even the exhaust manifold.
- Don’t Rush: An engine swap is a significant undertaking. Take your time, follow service manual procedures, and double-check everything.
Jeep XJ Engine For Sale: Estimated Price Table
Prices for Jeep XJ 4.0L engines vary widely based on condition, mileage, year, inclusions, and seller. This table provides a general estimate:
| Engine Type/Condition | Price Range (USD) | Typical Inclusions | Key Considerations & Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Used/Salvage (High Mileage) | $300 – $800 | Long block (engine core) | 150,000+ miles. High risk. Best for core, rebuild, or if verified running. Often from junkyards. |
| Used/Salvage (Low Mileage) | $800 – $1,800 | Long block, sometimes partial accessories | Under 100,000 miles. Less risk, but still "as-is." Verification of mileage is key. |
| Remanufactured (Standard) | $2,000 – $3,500 | Long block, new internals, tested | Professional rebuild, often with 3-year/100k mile warranty. Requires core return. |
| Remanufactured (Performance) | $3,500 – $5,000+ | Long block, upgraded components | Higher compression, cam, porting. For enhanced power. Specific builders. |
| New Crate (Custom/Specialty) | $5,000+ | Complete engine, often custom specs | Very rare for stock XJ. Often built for specific high-performance applications. |
Disclaimer: These are estimated ranges. Actual prices will vary based on location, seller, market demand, and the exact condition/inclusions. Always get a detailed quote. Shipping costs (often $200-$500+ for freight) are usually not included in the engine price.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What’s the main difference between a Renix and an HO 4.0L engine?
A1: The primary difference is the engine management system (ECU, sensors, and wiring harness) and cylinder head design. Renix (1987-1990) uses a unique system, while HO (1991-2001) uses a Chrysler-designed system with improved flow. Swapping between these types requires significant electrical and sensor modifications.
Q2: Can I put a newer 4.0L HO engine into an older XJ (e.g., a 2000 engine into a 1995 XJ)?
A2: Yes, it’s possible, but not always a direct bolt-in. While the block and basic mounts are similar, you’ll need to address differences in the cylinder head (especially for 2000-2001 coil-on-plug engines), intake/exhaust manifolds, sensor locations, and potentially the accessory drive system. You’ll often need to use your original intake, exhaust, and accessory components, and ensure sensor compatibility with your original wiring harness and ECU.
Q3: What’s the difference between a "long block" and a "short block"?
A3:
- Short Block: The engine block assembly, including the crankshaft, connecting rods, and pistons. It does not include the cylinder head(s), oil pan, valve cover, or any external components.
- Long Block: Includes the short block plus the cylinder head(s) (with valvetrain), oil pan, and valve cover. It typically does not include the intake manifold, exhaust manifold, accessory components (alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor), or sensors. This is the most common way engines are sold.
Q4: What should I budget for a complete XJ engine swap (engine + parts + labor)?
A4:
- DIY Swap: $1,000 – $4,500+. This range depends heavily on whether you buy a used ($300-$1,800) or remanufactured engine ($2,000-$4,000) and the cost of new ancillary parts (gaskets, fluids, etc., typically $300-$800).
- Professional Swap: $3,000 – $7,000+. This includes the engine cost, ancillary parts, and shop labor (often 15-25 hours at $100-$150/hour).
Q5: How long does an XJ engine swap typically take?
A5: For an experienced DIY mechanic with proper tools (like an engine hoist), it can take a dedicated weekend (2-3 days, 20-30 hours). For a novice, it could be a week or more. A professional shop can often complete it in 2-4 days.
Q6: Are there any common issues to look for in a used 4.0L engine?
A6: Yes, even the 4.0L has its quirks:
- Cracked Cylinder Head (0331 casting): Primarily affects 2000-2001 4.0L engines. Look for coolant consumption or milky oil.
- Rear Main Seal Leaks: Very common, but usually not catastrophic. Easy to fix during a swap.
- Lifter Noise/Tick: Can indicate worn lifters or a cam lobe.
- Low Oil Pressure: Can indicate worn main/rod bearings.
- Excessive Blow-by: Indicates worn piston rings or cylinder walls.
Conclusion
Finding a Jeep XJ engine for sale is more than just a transaction; it’s an investment in keeping a piece of automotive history alive. The legendary 4.0L I6, with its robust design and plentiful parts availability, makes an engine swap a viable and often rewarding endeavor. By understanding the different types of engines, knowing where to look, carefully considering compatibility, and budgeting for all associated costs, you can confidently navigate the process.
Whether you’re rescuing a beloved daily driver or breathing new life into a project rig, a successful engine swap ensures that your iconic Jeep Cherokee XJ will continue to conquer trails and turn heads for many years to come. Do your research, ask the right questions, and soon you’ll be back on the road, enjoying the timeless appeal of your XJ.